Researchers translated the language of plants!

Years have passed since the discovery that plants can communicate with each other; But until today, the method of this connection remained a mystery, and now a team of Japanese researchers revealed this secret of nature.
According to ISNA, it may not be visible to the eye, but the dust layer consisting of suspended particles in the air covers the surface of the plants, and it is these dust particles that allow plants to communicate with each other; Also, in some cases, plants use these particles to protect themselves. The compounds that sit on the surface of plants repel hungry creatures as a repellent, and it may be hard to believe, but when invaders approach, these particles warn the plants!
Scientists have known since the 1980s that plants have such a defense system, and since then this defense system has been identified in more than 80 plant species. However, the research was not able to answer the question of how plants receive messages and was only successful in answering the question of how plants send messages.
A mustard plant responds to airborne danger signals emitted by another plant.
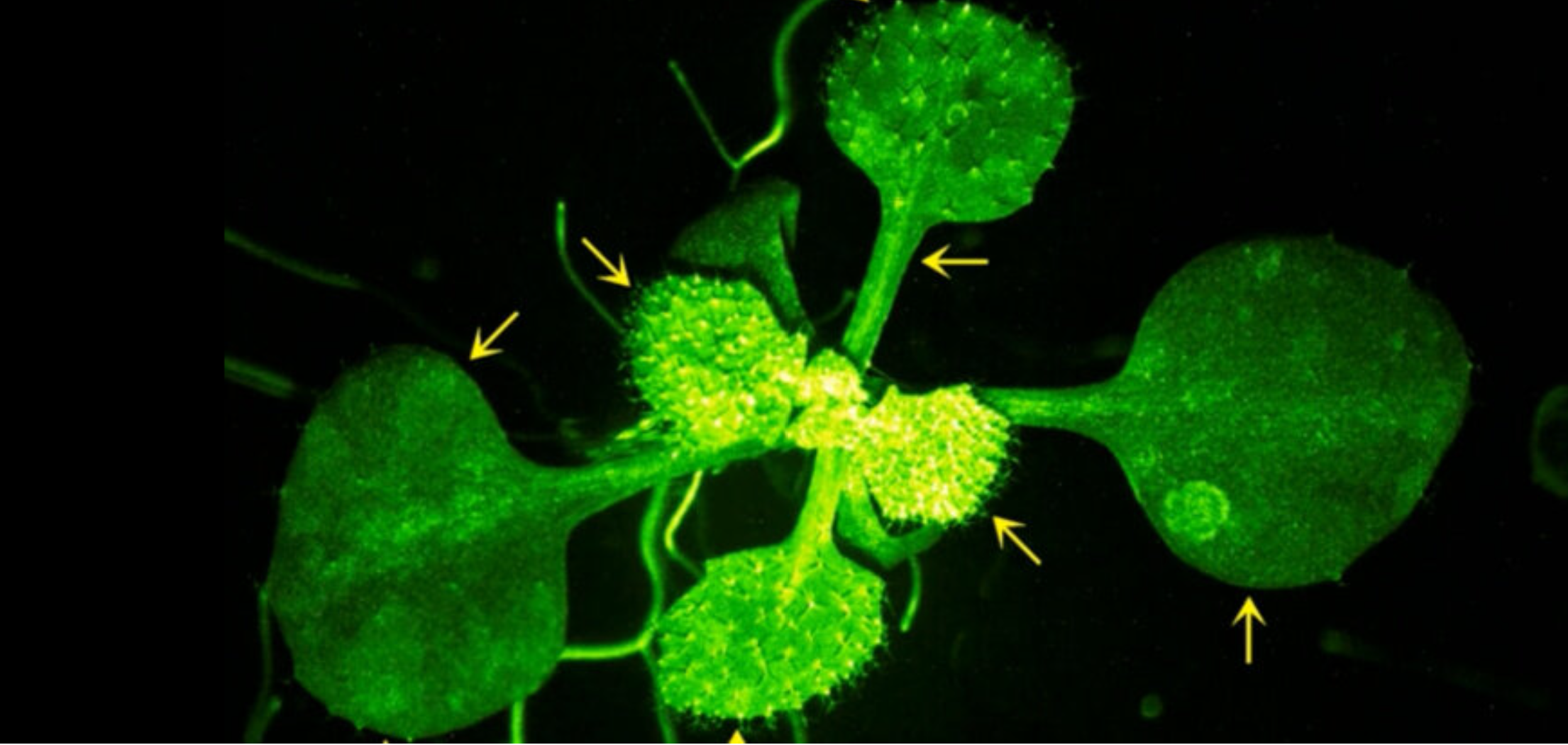
Now, a team of Japanese researchers has used real-time imaging techniques to identify how plants receive and respond to these alerts; In these experiments, scientists placed compounds emitted from damaged and insect-infested plants onto their damaged neighbors and built a fluorescence microscope to watch what happened.
Scientists studied a type of grass that belongs to the mustard family and is called “Arabidopsis”. It was discovered that the plant is not a normal grass but has been genetically modified; So its cells contained a biosensor that turned green when calcium ions rushed toward it. Calcium signaling is something that human cells also use to communicate.
With the help of these methods, scientists were finally able to unravel the complex story of when, where and how plants react to the “warning messages” of their neighbors in the air. This communication network, which is hidden from our view, plays an essential role in the timely protection of neighboring plants against imminent threats. By analyzing the compounds in the air, the researchers found that two compounds called Z-3-HAL and E-2-HAL induce calcium signals in the plant.
The set used to receive plant signals
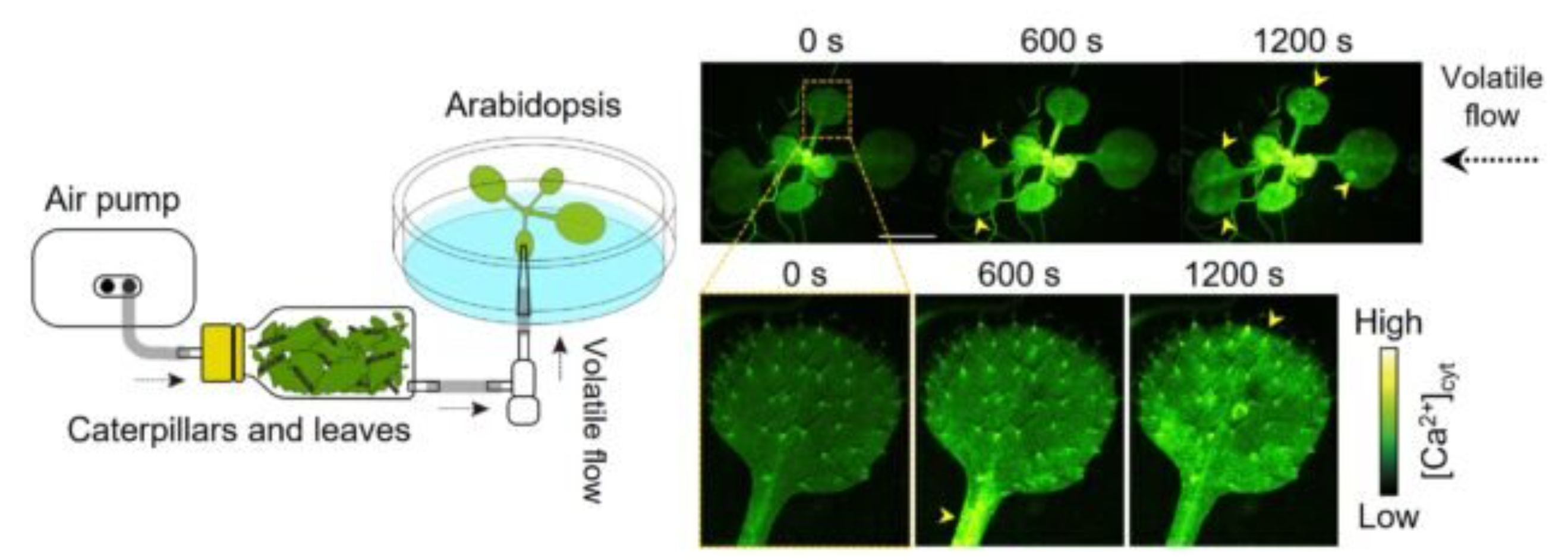
The researchers also looked at which cells first respond to danger signals and found that guard cells are bean-shaped cells on plant surfaces that form stomata. They are exactly the same small pores that open during plant photosynthesis.
When Arabidopsis plants were exposed to Z-3-HAL, guard cells produced calcium signals within a minute or so, after which mesophyll cells received the message. After the hazard is removed, calcium signaling is significantly reduced, indicating that the stomata function as the plant's nostrils.






