Ibn Haitham, scientist of light physics
 Ibn Haytham
Ibn HaythamAn abstract of Ibn Haitham's biography:
Full name: Abu Ali Muhammad bin Hasan bin Haitham Basri
Date of birth: 354 Hijri
Place of birth: Basra
Field of activity: mathematician, astronomer, physicist, philosophy, theology and medicine
Died: 430
Tomb: Cairo
 Biography of Ibn Haitham
Biography of Ibn HaithamBiography of Ibn Haytham:
Abu Ali Muhammad bin Hasan bin Haitham Basri was born in Basra in 354 AH. He was one of the greatest mathematicians and undoubtedly the best Arab or Iranian Muslim physicist. This scientist is known as In Haitham and is known as the first light physics scientist in the world. He has played an important role in the field of knowledge of light, the laws of refraction and its reflection, on the other hand, he has had a hand in the sciences such as astronomy, geometry, ophthalmology, and the optical solution of eye problems.
Ibn Haytham was fluent in Arabic and had a good handwriting. The books he used to copy, apart from the beautiful handwriting, also had a lot of scientific accuracy and the Taliban paid a lot of money for these books.
Despite the fame of this scientist, not much information is available about the different periods of his life, the professors of his education in general. What there is about his biography are the traditions that were narrated about three centuries ago.
 Ibn Haitham's writings
Ibn Haitham's writingsEducation of Ibn Haitham:
Ibn Haytham, seeing the differences between people, decided to study philosophical sciences after studying natural sciences on the way to the truth.
Sheikh Alamuddin Qaiser bin Abi al-Qasim al-Muhandis narrates; Ibn Haitham in Basra, which at that time was under the command of Al-Buyeh of Iraq; He had a judicial job and then he was assigned to the Ministry of Basra, but since he preferred science to other works, he drove himself crazy so that he would be removed from his position. After this, he will go to Egypt.
According to what Qafti states; Ibn Haytham's trip to Egypt with the encouragement and promises of the ruler of Egypt; Al-Hakim Fatimi has been done. Of course, it is not far from expected that Ibn Haytham made this trip in order to implement his plan to regulate the water of the Nile and enjoy the grace of the ruler.
Qatfi says that the king, knowing about Ibn Haytham's plan, sent him a budget. Ibn Haytham reached that country, the king also went to welcome this scientist. Shortly after this journey, Ibn Haytham along with a group of engineers set out to investigate the Nile and its channel in the high part of southern Egypt.
After observing the works and buildings of the Egyptians, which were built based on precise geometric designs, he realized that if the design he considered was feasible, the cultured Egyptians would have implemented it before him, so he expressed his disappointment to the Caliph. It seems that the caliph did not show a strong reaction, but he was so angry that instead of appointing Ibn Haytham alongside great men such as Ibn Yunus, he was assigned to civil jobs in Cairo's Dar al-Hikma.
Afraid of this king, Ibn Haytham joined the civil service, but in order to get rid of it, he decided to drive himself crazy again, for this reason, the caliph confiscated Ibn Haytham's property, appointed someone to take care of him, and appointed this scholar locked in his house.
With the death of the caliph in 411 AD, Ibn Haytham also stopped pretending to be insane, was freed, and got his property back. After this incident, he settled in a place near Cairo and spent the rest of his life teaching and writing his works.
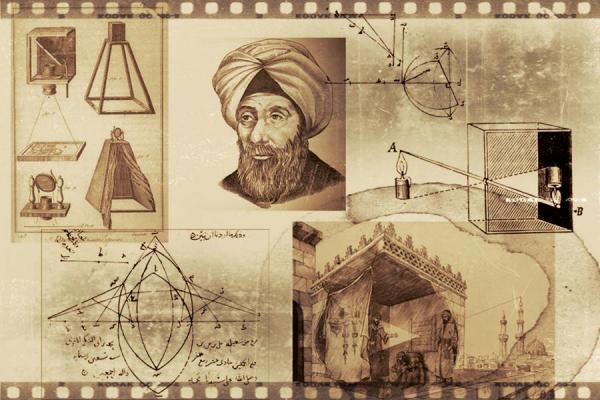 Ibn Haytham; Light physicist
Ibn Haytham; Light physicistBayhaqi believes that Ibn Haytham wrote a treatise on the regulation of Nile water and then went to Egypt, but the governor called it useless and expensive from the very beginning of his arrival and examination of his plan. Ibn Haytham also flees to Syria at night, fearing the caliph, to serve one of the rulers of that land. Despite the blessings that this ruler had, he was satisfied with a small amount and devoted himself to scientific work.
Shahrzuri, after repeating Bayhaqi's words, narrates another narration according to which Ibn Haytham first lived in Syria and then went to Egypt from there. On the other hand, it does not seem that Ibn Haytham stayed in Cairo all his life until the death of al-Hakim, this is clear from the answer he gave to a geometrical question in 418 in Baghdad, so he was in Baghdad at least until that year. but he returned to Egypt again, because Qazi Abu Zayd Abd al-Rahman bin Isa saw him in that country in 430.
Ibn Haitham's scientific method:
Ibn Haitham is known as the first scientist of his era who uses scientific evidence to check his theories, because in that era, physics was not accompanied by scientific experiments like the science of philosophy. He is the first scientist who stated the necessity of having empirical evidence to accept a theory, in fact his book Optics was a criticism of Ptolemy's Al-Magist book.
After a thousand years, this book is taught and introduced as a source by the masters of this science. Some historians of this science believe; Esnel's law in optics actually originates from the research of Ibn Sahl and Ibn Haytham.
The invention of the magnifying glass by Ibn Haytham:
Ibn Haytham was the first to invent the magnifying glass, this object eventually led to the invention of glasses by Roger Bacon, as this scientist studied Ibn Haytham's works.
 The invention of the magnifying glass by Ibn Haytham
The invention of the magnifying glass by Ibn HaythamThe dark room and Ibn Haitham:
The explanation of the principles of the dark room and the invention of the magnifying glass are some of the outstanding works of this scientist, which eventually led to the construction of the photographic camera.
To study the solar eclipse, he invented a tool called the dark box, during the Crusades, this tool was transferred to Europe. A dark room is a room that only had a small opening on one of its surfaces. When the light passed through the opening, a relatively clear image was formed upside down on the opposite surface.
The dark room attracted the attention of painters, all painters, especially the Italians of the 16th century, used this device to accurately design landscapes and see the correct perspective. In this way, they placed a paper on the surface opposite the aperture and painted the formed image, these images were very real and had a correct depth (perspective).
 The invention of the dark room by Ibn Haytham
The invention of the dark room by Ibn HaythamDeath of Ibn Haytham:
There is no information about the exact date of death of this scientist, most writers believe that he died around 430 AD or later in Cairo, based on what Bayhaqi states, he died due to his severe illness, he himself slept in front of the Kaaba. He said the truth and finished.
Ibn Haytham had a hand in mathematics and optics, speech, metaphysics, logic, ethics, literature and music, and he had something to say especially in theoretical laws and general medical matters. Ibn Haytham did not practice medicine, and Ptolemy II called him “Bayhaqi” and mentioned his religious asceticism.
Students of Ibn Haitham:
Among the students that Ibn Haytham had during the years he was teaching, we know two people; Abolufa Mubasher bin Fatek, who was a famous Egyptian scientist and continued to study mathematics under Ibn Haytham, and his other student is known as Sohrhab (Sohrab), and he was one of the elders of Semnan, who studied under Ibn Haytham for three years and was the master of every He used to charge him one hundred dinars per month, but when the lesson was over, Ibn Haitham returned all that he had taken to Sarkhab Baz and reminded him that his intention was to test the student's purity in learning.
Ibn Haytham's works:
The most important works of this scientist can be mentioned as follows:
– Al-Muhammad; which is his most famous book.
– Extracting the height of the pole at the end of the investigation.
– Extracting the direction of the Qibla in all the inhabited areas with tables and adjectives and the evidence for it.
– Aleh Lafass of light and refraction.
– Moon movement
– Barkar Al-Dawer al-Athawa or using a burjal (Berkar) to draw Al-Dawaar Al-Athawa
– Message in the space of Al-Massim al-Makafi
– A message in the form of al-Kosuf
– Al-Muraya al-Muharagha with circles
– Article in Hayat al-Alam
– Definitely burning mirrors
– A brief article on the forms of the crescent and an excerpted article on the forms of the crescent
– Solving doubts about the movement of rotation
– Doubts on Ptolemy
– Major extraction of mountains
– Planetary lights.
– Squaring the circle
– the light
– Moonlight
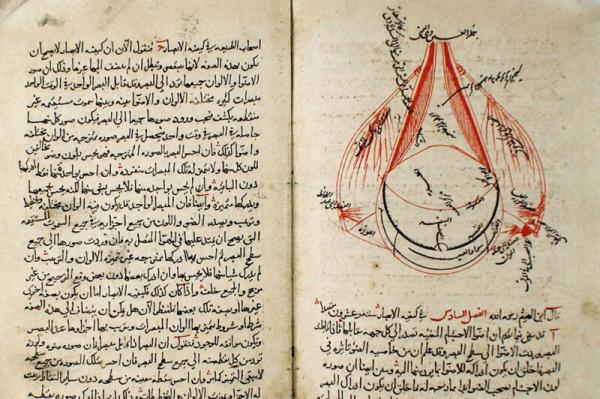 The works left by Ibn Haytham
The works left by Ibn Haythamcompilation: Cover biographical section






