Father of modern surgery science; Abolghasem Zahrawi
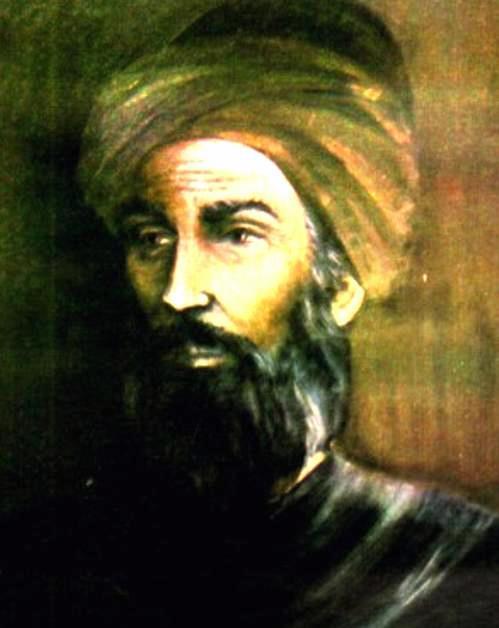
 Abolghasem Zahrawi
Abolghasem ZahrawiA summary of Abolqasem Zahrawi's biography:
Full name: Abu al-Qasim Khalaf bin Abbas al-Zahrawi
Date of birth: 936 Hijri
Place of birth: Al-Zahra, Spain
Nationality: Spanish
Profession: doctor and surgeon
Fame: Father of modern surgery
Works: Al-Tasrif Laman Ajr an al-Taalif
Died: 1013 AH
Buried: Cordoba, Spain
 Abolghasem Zahrawi's biography
Abolghasem Zahrawi's biographyAbolghasem Zahrawi's biography:
Abu al-Qasim Khalaf bin Abbas al-Zahrawi is a doctor from the fourth century who was born in the year 936 AH in the city of Al-Zahra, Spain. Zahrawi's name is given in different languages under different titles, among which we can mention Bucasis, Albucasis, Abulcasis Sezgin, all these names are different interpretations of this doctor's nickname. A group of Ansar were considered his successors who had migrated from Medina to Andalusia.
Scientific sources about Abolghasem Zahrawi:
The closest scientific source to the life of this thinker is the writings of Abu Muhammad Ali bin Ahmad bin Said, who became known as Ibn Hazm. The only work left by Zahrawi; Al-Tasrif Leman is an author who is highly respected in the medical field.
Other information about Zahrawi's life are almost the same as those given by Ibn Hazm about the importance of Kitab al-Tasrif. Some of the life data of this scientist are obscure.
In the meantime, the writings of Leo African complement the information about this scientist, among these things, we can mention Zahrawi's life for 101 years and special medicine for Mansourbollah. It seems that Mansour Balleh is the same Ibn Abi Amir Mansour, who was the minister of Hisham II, the ruler of Andalusia.
Other reports that exist about Zahrawi are almost all about the importance of his opinions in medicine and authoring the book of al-Tasrif.
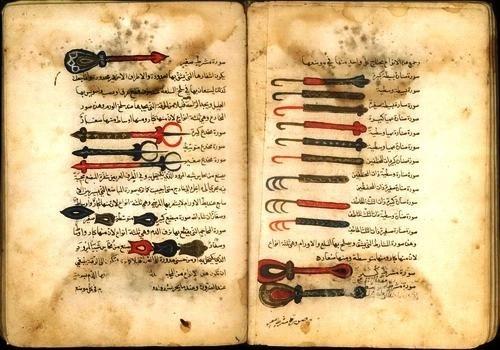 Abolghasem Zahrawi; The famous Andalusian doctor
Abolghasem Zahrawi; The famous Andalusian doctorAbolghasem Zahrawi's students:
The sources mention two people who were probably among Zahrawi's students, including Abdurrahman ibn Muhammad ibn Abd al-Kabir ibn Yahya ibn Wafed Lakhmi, known as Ibn Wafed, and Ahmad ibn Yahya ibn Sumayq al-Qurtubi, known as Ibn Sumayq. Ibn Wafed was a physician and pharmacist, and Ibn Samiq was an Andalusian writer and physician.
Abolghasem Zahrawi's lasting work:
According to what Zahrawi states in the beginning of his book, al-Tasrif was written for the use of all members of society, including men and women, specifically and generally. The book contains thirty articles, which can be divided into four parts. At first, the first article of the book, which contains general information about medical knowledge and the reason for naming the book, the author's purpose for writing the book.
The second part forms the second article of the book, which narrates about pathology and their classification in the medical knowledge of the Islamic period. In this article, Zahrawi mentions a wide range of diseases of the human body, starting from head to toe, and then to diseases of women, children, adults, joint diseases, diseases that occur due to factors outside the body, such as injuries and Fractures and poisoning also indicate skin diseases. The last topic of this article tells about the types of fevers.
In the third part of al-Tasrif, the third to the 29th articles are given, in which Zahrawi provides information about pharmacology and the description of a wide range of drugs such as antidotes, laxatives, syrups, powders, tablets and ointments.
The fourth part of the book, which is actually the distinguishing feature of Al-Tasrif from other books before and after him in the Islamic era, is related to the 30th article, which consists of three chapters and fully narrates about the issues and works of healing by hand. slow This chapter is against drug treatments.
In the first chapter, he has dealt with a set of treatments including heating (= kay), in the second chapter, treatment by splitting (= batt) and surgical methods, and in the third chapter, the treatment of fractures (= jabr). Zahrawi uses images and a wide collection of tools for heating, splitting, surgery and all kinds of fracture treatment tools along with unique explanations. Of course, the number of these images is different in different manuscripts.
In the only complete edition of the book that exists, 198 simple and composite illustrations are given. Following the translation of the 30th article, in the Middle Ages, illustrations of the Arabic text of the book became popular in European medicine.
In al-Tasrif, Zahrawi uses the works and opinions of a large collection of doctors before him, including Greek doctors and Islamic period. Among these people, we can mention Dioscorides, Hippocrates, Akriton, Akriton, Galen, etc., all of whom were among the famous doctors of Bonai. The most references are given to Galen and eleven titles of his works are given, including al-Dawiya al-Murkabah.
Ibn Jajar was one of the doctors of the Islamic era, which is a collection of seven books, including Fi-al-Baha. Ibn Masawiyyah along with five books of his including fi al-ashal, Ishaq bin Sulaiman Israeli with the book al-Hummiyat are among other references. In the meantime, the most references of this scientist are to the doctor who is almost his contemporary, Muhammad bin Zakaria Razi. However, there are quotes from Bolus by Zahrawi that have received the most attention.
Many consider the general methods of treating septicemia as boluses.
 The lasting works of Abolghasem Zahrawi
The lasting works of Abolghasem ZahrawiThere are many manuscripts left by al-Tasrif Abul Qasim Zahrawi, among them, a book titled Aqaqir, Amaar al-Aqaqir and Amaar al-Adawiya al-Mufarda are attributed to this scientist, but all of them are part of the 29th article of al-Tasrif, which deals with the duration of the therapeutic effect. Medicines have been brought. The manuscript of the 30th article is presented in the form of a separate book under the title of Al-Jarrah, and apart from printing a photo of the text of the book, other prints of the book including part or parts of it are included.
Chapter 30 of Kitab al-Tasrif was translated into Farsi by Mehdi Mohaghegh under the title of surgery and its tools. Lacker also translated the 30th article into French, the English translation of this book was done by Spink and Geoffrey Lewis in London.
The oldest Latin translation of the 30th article is related to the Middle Ages and Gerard of Cremona. This translation along with pictures from the translation of the Arabic text has been transferred to Europe, which ultimately left a tremendous impact on Europeans' familiarity with Islamic medicine. This translation, along with a text about surgery, written by the French doctor, Guy de Chauliac, has been printed several times in Europe. The combination of Gérard's translation with Shuliac's text shows more than anything that he was influenced by Gérard's text.
28 articles on the subject of medicine and pharmacology were written and translated into Latin by Simon Genovese and Abraham Tortosai, which were published several times in the Middle Ages.
Regarding the influence of a group of medieval doctors on Zahrawi's achievements, many researches have been done, especially the Book of Interpretation and various parts of the book that have been examined.
Some of the surgical instruments in the CM article have been recreated by Sezgin in an exhibition using modern knowledge and materials.
 Abolghasem Zahrawi renovated surgical instruments
Abolghasem Zahrawi renovated surgical instrumentsOther activities of Abolghasem Zahrawi:
A report has been received from Naviri that shows quotes about the creation of perfume by Zahrawi, so it can be said that the possibility of other books by this scientist is very high. Despite the structural and thematic similarity with Zahrawi's opinions in some parts of al-Tasrif, these phrases and quotations of Nuiri are not exactly similar to the quotations of al-Tasrif. On the other hand, there are quotes about Abu al-Qasim Khalaf bin Abbas Nahrawi and the attribution of a book on agriculture to him. This book is similar to other important works in this field, including the works of Ibn Awwam, who was an Andalusian botanist, and Abu Umar Ahmad bin Muhammad bin Hajjaj of Esbile, whose Arabic originals have not been found yet, but Spanish translations are available.
Samso and Vernet Khines, assuming that Nahrawi is the corrected form of Zahrawi's name, believe that Zahrawi, by authoring this work (in addition to medical knowledge), was also the source of producing scientific works in the field of agriculture in Andalusia.
 Abolghasem Zahrawi's activities
Abolghasem Zahrawi's activitiescompilation: Cover biographical section






